Remote services
Hive SDK provides Remote Services that allow you to perform tasks that should originally be done on the game server remotely through Hive Console. The Remote Services provided in Provisioning are as follows.
- Remote Configuration
- Remote Logging
Remote configuration¶
When operating a game app, the game server URL may vary depending on the game app version. Remote Configuration is a feature that allows you to change the server URL settings remotely without accessing the game server. You can register server URL information in Hive Console and map and manage servers by game app version.
Note
Remote Configuration is a feature that allows you to remotely modify server settings that need to be changed on the game server through Hive Console, and currently only supports the ability to remotely modify the game server URL. Other Remote Configuration features will be added in the future.
The game server URL can be modified differently for each AppID, game app version, and server. To use Remote Configuration, you must first register the server URL in Hive Console.
When you call Configuration.getMetaData from the game client, you can receive the server URL registered or modified in Hive Console as a String value. Here is an example code that calls the server URL.
API Reference: HiveConfiguration getMetaData
API Reference: Configuration:: getMetaData
#include <HIVE_SDK_Plugin/HIVE_CPP.h>
using namespace std;
using namespace hive;
// data key
string key = "game_server_url";
// Whether data is updated
bool forceReload = false;
// 메타데이터 호출
Configuration::getMetaData(key, forceReload, [=](ResultAPI const & result, string value) {
if (result.isSuccess()) {
// 호출 성공
}
});
API Reference: Configuration.getMetaData
import com.hive.Configuration;
import com.hive.ResultAPI;
// data key
val key = "game_server_url"
// Whether data is updated
val forceReload = false
// metadata call
Configuration.getMetaData(key, forceReload, object : Configuration.GetMetaDataListener {
override fun onGetMetaData(result: ResultAPI, data: String) {
if (result.isSuccess) {
// call successful
}
}
})
API Reference: Configuration.INSTANCE .getMetaData
API Reference: ConfigurationInterface.getMetaData
API Reference: HIVEConfiguration getMegaData
#import <HIVEService/HIVEService-Swift.h>
// data key
NSString *key = @"game_server_url";
// Whether data is updated
BOOL forceload = NO;
// metadata call
[HIVEConfiguration getMegaData: key forceReload: forceReload handler: ^(HIVEResultAPI *result, NSString *value) {
if ([result isSuccess]) {
// call successful
}
}];
#include "HiveConfiguration.h"
// Data key
FString Key = TEXT("game_server_url");
// Data refresh status
bool bForceReload = false;
// Meta data call
FHiveConfiguration::GetMetaData(Key, bForceReload, FHiveConfigurationOnMetaDataDelegate::CreateLambda([this](const FHiveResultAPI& Result, const FString& Value) {
if (Result.IsSuccess()) {
// Call successful
}
}));
Using cached values¶
Hive SDK reads the server URL previously entered in Hive Console during the initialization process and caches it for the game client. Therefore, to reduce network costs by using this cached value when you want to retrieve the previously entered value without changing the server URL in Hive Console, set forceReload to false when calling Configuration.getMetaData.
If you have modified the server URL in Hive Console and need to reflect this modified URL in the game app, set forceReload to true when calling Configuration.getMetaData. This will delete the existing cached server URL in the game client and fetch the latest server URL from the Hive server. This calling pattern is generally used when the game app is restarted.
Remote logging¶
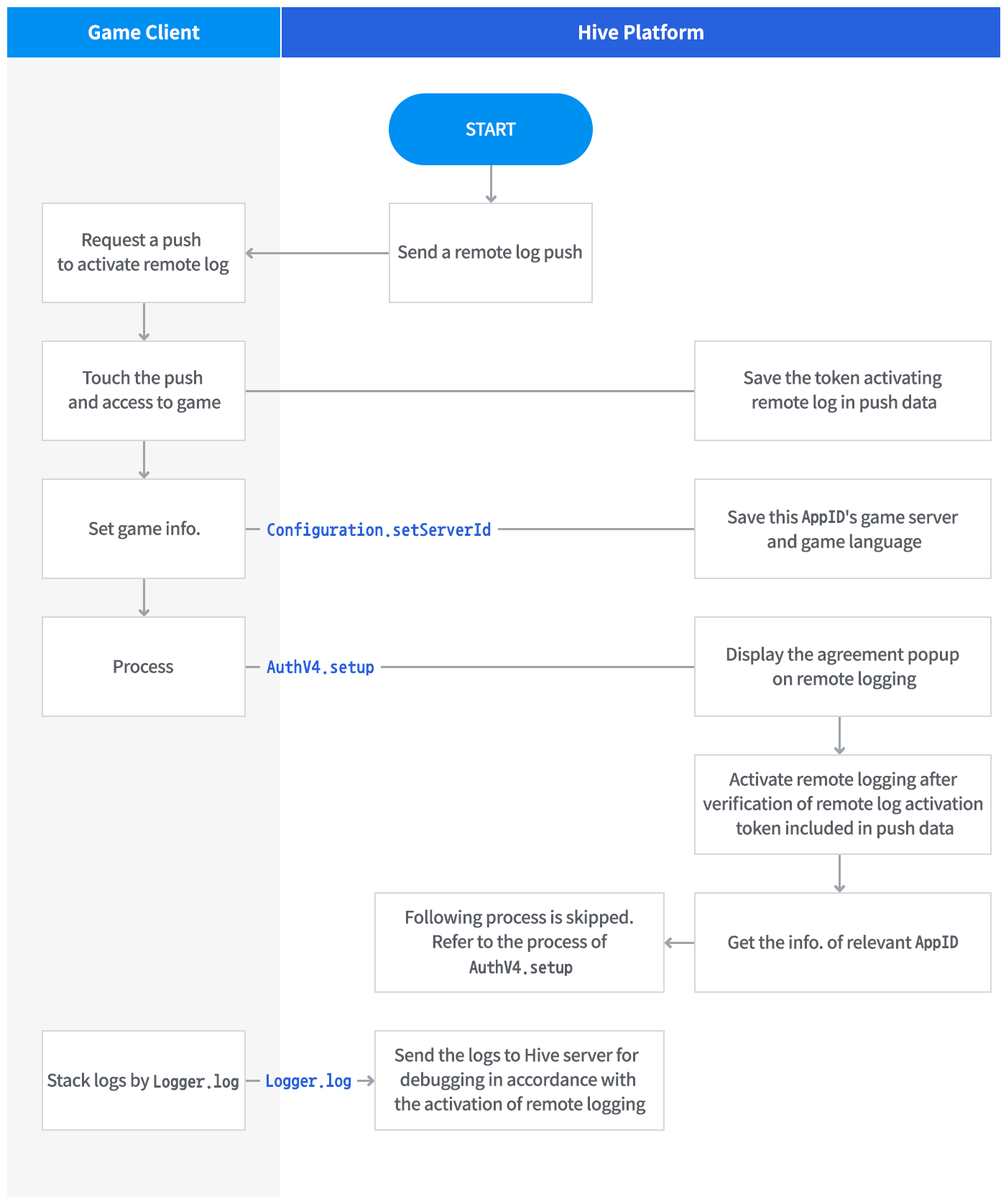
Remote Logging is a feature that allows logs that need to be collected from the game server to be collected remotely via Hive SDK. By using Remote Logging, you can receive debug logs remotely. For example, if you register a specific game app user in Hive Console, you can check the debug logs in a remote environment when issues related to this user occur, rather than on the game server.
When you specify a specific user to collect logs, the game app logs and Hive logs accumulated when this user uses the game app are collected and loaded into Google Cloud. You can receive the logs collected remotely to monitor and use for debugging. To use Remote Logging, you must first set up the user to collect logs in Hive Console.
How it works¶
The Remote Logging operation works as follows.
Target user settings¶
Users who can collect logs are those who have issued a DID after running the game app at least once (i.e., Hive SDK has been initialized at least once). However, if a crash or error occurred before initializing Hive SDK during the game app execution process, logs cannot be collected from this user.
Collecting logs¶
Enabling Remote Logging will collect Hive logs and game app logs for the duration of log collection entered in Hive Console.
Warning
If you collect too many logs, resources may be concentrated on network traffic and log processing, which can affect game app performance. It is recommended to minimize repetitive logs occurring within loops or to consolidate them into a single log for collection.
Hive log¶
Hive logs are logs that are collected by default within Hive SDK code. They cannot be controlled by the game app.
Game app log¶
Game app logs are logs obtained by inserting the Logger.log call provided by Hive SDK into the game client code. You can choose the desired location in the game client code to collect the desired values. Insert code like the example below at the desired location.
API Reference: Logger.log
API Reference: Logger::log
API Reference: Logger.i
API Reference: LogInterface.log
API Reference: Objective-C